ANIMAL TISSUE
PREPARED BY MR.
ABHIJIT DAS
INTRODUCTION
Tissue consists of group of similar cells along with their intercellular matrix performing a specific function.
These tissues are organized in specific proportion
and pattern to form an organ like stomach,
lung, kidney, heart etc.
When two or more organs perform a common function by
their physical and chemical interaction, they together form organ system such as digestive system, respiratory
system, cardiovascular system etc.
Cells, tissues, organs and organ systems split up
the work (division of labour) and contribute
to the survival of the body as a whole.
Tissues are broadly classified into four types:
·
Epithelial tissue
·
Connective tissue
·
Muscular tissue
· Neural tissue
EPITHELIAL TISSUE
Ø This
tissue has a free surface which faces either a body
fluid or air thus provides a covering or a
lining for some part of the body.
Ø The
cells are tightly packed with little
intercellular matrix.
Ø There
are two types of epithelial tissues; simple
epithelium and compound epithelium (or stratified epithelium).
Ø Simple
epithelium is composed of a single layer of cells.
Ø Stratified
epithelium consists of two or more layers
and has protective function as it does in our skin.
Figure Credit: Jayashree Baidya
On the basis of structural
modification of cells, simple epithelium is
further divided into 3 types.
·
Squamous epithelium
·
Cuboidal epithelium
·
Columnar epithelium
SQUAMOUS EPITHELIUM
Figure Credit: Jayashree Baidya
The squamous epithelium is made of a single layer of
flattened cells.
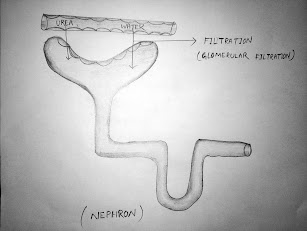
They are involved in functions like forming a diffusion boundary and filtration
boundary.
They are found in the walls
of blood vessels and alveoli of lungs.
Figure Credit: Jayashree Baidya
CUBOIDAL EPITHELIUM
Figure Credit: Jayashree Baidya
It is composed of a single layer of cube like cells.
Its main functions are secretion and absorption.
Location: Ducts of
glands and tubular parts of nephrons (DCT) in
kidneys.
The epithelium of proximal convoluted tubule (PCT)
of nephron in the kidney has microvilli. That’s why the tissue present at PCT
is known as BRUSH BORDER CUBOIDAL EPITHELIUM.
Figure Credit: Jayashree Baidya
COLUMNAR EPITHELIUM
Figure Credit: Jayashree Baidya
It is composed of a single layer of tall and slender (thin) cells.
Free surface may have microvilli (BRUSH BORDER
COLUMNAR EPITHELIUM).
They help in secretion and absorption.
Location: stomach(columnar epithelium) and small intestine(brush border columnar epithelium).
Figure Credit: Jayashree Baidya
CILIATED EPITHELIUM
CILIA: hair like structure (not
a part of cytoplasm)
If the columnar and
cuboidal cells bear cilia on their free surface they are called ciliated
epithelium.
Their function is to move
particles or mucus in a specific direction over the epithelium.
Location of ciliated cuboidal epithelium: lower
respiratory tract.
Location of ciliated columnar epithelium: upper
respiratory tract, ovary (fallopian tube).
Figure Credit: Jayashree Baidya
CONNECTIVE TISSUE
They are named connective tissues because of their
special function of linking and supporting other
tissues/organs of the body.
They are most abundant and
widely distributed throughout the body.
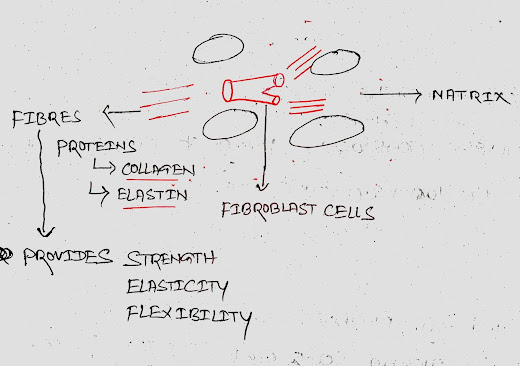
In all connective tissues except blood, the
fibroblast cells secret fibres which are
structural proteins (collagen/elastin).
The fibres provide strength, elasticity and flexibility to the tissue.
The matrix of
connective tissues are made up of proteins and
carbohydrates.
Connective tissues are classified into three types:
·
Loose connective tissue
·
Dense connective tissue
·
Specialised connective tissue
LOOSE CONNECTIVE TISSUE
In this tissue cells and fibres are loosely arranged.
It is further divided into two
categories:
·
Areolar tissue
·
Adipose tissue
AREOLAR TISSUE
Areolar tissue present beneath the skin.
It provides support to epithelium.
It is the weekest and most abundant.
ADIPOSE TISSUE
Adipose tissue stores fat.
It is also known as fat tissue or fatty tissue that
is mainly composed of fat cells called adipocytes.
Adipocyte contains large globules of fat known as lipid droplets.
Adipocytes are predominantly found around the organs in the abdominal
cavity.
Adipose tissues are also
located beneath the skin.
The excess of nutrients which are not used
immediately are converted into fats and are stored in this tissue.
DENSE CONNECTIVE TISSUE
In this tissue cells and fibres are compactly or densely arranged.
It is further divided into two categories:
·
Dense regular tissues
·
Dense irregular tissues
Tendons and ligaments are examples of dense regular tissues. Tendons attach skeletal muscles to bones and ligaments attach one bone to another bone.
Dense irregular connective tissues provide covering to other structures such as pericardium (covering of heart), periosteum (covering of bone), and perichondrium (covering of cartilage).
SPECIALISED CONNECTIVE TISSUE
Skeletal connective tissues and
fluid connective tissues come under specialised
connective tissue.
Bone and cartilage are two types of skeletal connective tissue.
Blood and lymph are two types of fluid connective tissue.
BONE
Bones are hard and non-pliable.
Bones are rich in calcium
salts and collagen fibres which give bone
its strength.
Bone is the main tissue that provides structural frame to the body.
Bones support and protect other tissues and organs.
The bone cells (osteocytes)
are present in the spaces called lacunae.
Red bone marrow is the site of production
of blood cells.
CARTILAGE
Cartilage tissues are solid and pliable.
They are mainly of three types:
·
Hyaline cartilage
·
White fibrous cartilage
·
Elastic cartilage
HYALINE CARTILAGE
They are apparently
fibreless.
They are weakest and most abundant.
Location: C shaped rings of
trachea, end of long bones, larynx etc.
WHITE FIBROUS CARTILAGE
They contain collagen fibres. That’s why they are
the strongest.
Location: vertebral column.
ELASTIC CARTILAGE
They contain yellow elastic
fibres.
They are elastic in nature.
Examples of elastic cartilage: pinna of ear, tip of nose,
epiglottis, Eustachian tube
etc.
BLOOD
Blood is a fluid connective tissue containing blood
cells (RBC, WBC, platelets) and plasma.
It is the main circulating fluid that helps in the
transport of various substances.
MUSCLE TISSUE
Muscle cells are known as myofibres or muscle
fibres.
Myofibres can contract and relax providing movement
within the body (movement) and of the body (locomotion).
Muscle tissues are of three types:
·
Skeletal muscle tissue
·
Smooth muscle tissue
·
Cardiac muscle tissue
SKELETAL MUSCLE TISSUE
Skeletal muscle tissue is described
as skeletal because it is closely attached to
the skeletal bone.
They are also known as voluntary
muscles (because you can move them whenever you want).
They are otherwise known as striated
muscles because striations (stripes) can
be seen under microscopic observation.
Skeletal muscle cells are cylindrical
shaped and multinucleated (they have more
than one nucleus).
They are found in muscles of limbs, eyelids, tongue, abdominal wall
etc.
Skeletal muscle contraction is stimulated by motor
nerve impulses.
SMOOTH MUSCLE
Smooth muscles are found in internal
organs (visceral organs e.g. lungs, liver, pancreas, intestine etc.)
They are spindle shaped and
uninucleated.
They are also known as involuntary
muscle (you cannot move at will)
They are non-striated,
as they do not have any striation.
CARDIAC MUSCLE
This muscle is found in the wall
of heart.
They are branched and slightly
striated.
They are also uninucleated.
NERVOUS TISSUE/NEURAL
TISSUE
Two types of cells
are found in nervous tissue:
·
Neurons (excitable cells)
·
Glial cells (non-excitable cells)
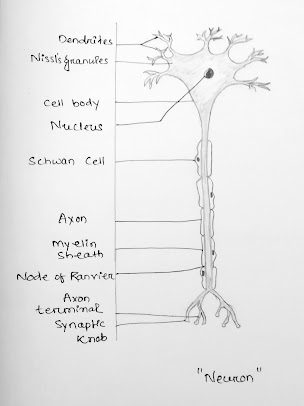
Neurons transmit signals/information.
Glial cells support the neurons.
Figure Credit: Yostnarani Sethy